Many business processes as well as your business success are increasingly relying on the continuous availability of your IT environment. As an IT expert, we take your business to the next level in a calculated and reliable way by which you will be gaining time for your core tasks and on top of it saving money.

Most common uses for managed services are telecommunications, printing infrastructure and networks. During the all-around monitoring of a server, including the environment belonging to it, the software and hardware checks will be running around-the-clock (24 x 7). Other tests, like checking the status of the daily backup, will be running on a daily base or, according to settings agreed upon, several times a day. All these checks will be running independently, without you as a user noticing anything.
Managed Services: : Always the all-included service package best fitting your IT company's needs.
-
Advantages for your company:
- predictable monthly fixed costs
- individual and modular designed solutions, tailored for your company's needs, among other things connectivity, security, data backup and archiving
- a high level and consistent quality of services
- a high level of transparency related to service and repair processes
- operational reliability and high availability concerning your IT environment
- optimization of IT service levels
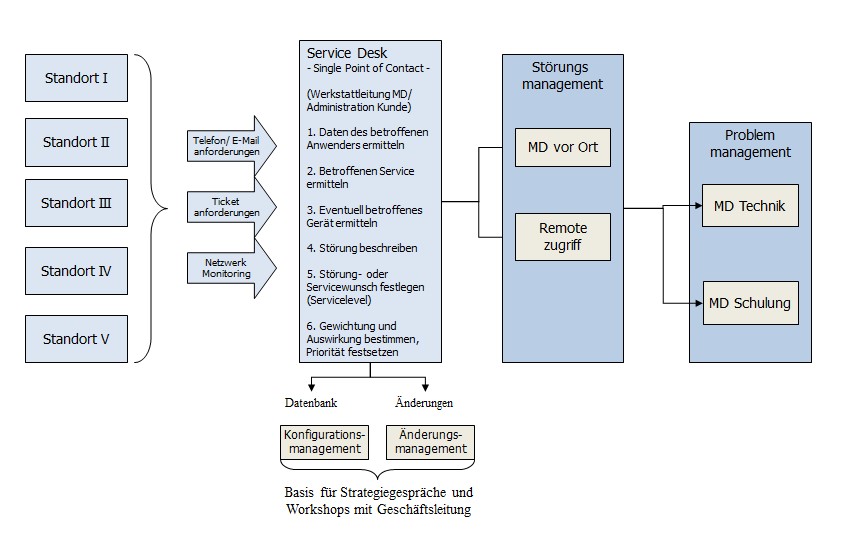
Incident management
The incident management process has the function of recording, and swiftly resolving, actual or foreseeable service impairments. Depending on the quality of the incident, one or more (definable) levels of support may be involved:
- Incident reporting and recording
- Classification, prioritization based on urgency and impact
- Checking for known fault patterns
- Analysis and diagnosis
- Elimination and service recovery
- Closing of the trouble ticket
The process also needs to provide for escalation procedures; for example, calling in further support levels (functional escalation) or alerting management levels (vertical escalation)
Problem management
A distinction must be made between incident and problem management. Incident management aims to restore the service as quickly as possible ? no matter how. The actual cause of an incident is not obvious in all cases. Sometimes the incident can be eliminated through a workaround; this would mean that the unidentified root cause would always lead to similar incidents. Preventing this is the task of problem management. A problem management process consisting of two stages is highly recommended:
- Problem control In the initial step, the cause is first discovered, that is, a known error is associated with the problem or the error is determined.
- Error control: In the second step, a meaningful solution is then sought for the error, the implementation is monitored, and the effectiveness of the solution is tested in order to be able to close the trouble ticket.
- Configuration planning: Defining the configuration management policy (scope, naming and versioning principles, etc.), design of the configuration management database for managing the configuration data.
- Identification: Identification of new or modified components with identifier, version level, state, classification or categorization
- Status monitoring: Tracking operating resource states, preventing unauthorized operations with operating resources
- Configuration check: Checking that the operating resource information is complete and up-to-date
- Verification: Determining target/actual deviations between planned/documented and actual configuration properties
- Documenting the hardware, applications, infrastructure
- Error information system specifically for the configuration items (log inventory)
- Decision-making support for investment projects
-
Configuration management
Configuration management ensures an integrated information base for all service management processes. This relates to information on the properties of the configuration elements used, such as applications, IT systems, infrastructure and its relationships, and information on logged incidents.
The following procedures should be ensured as part of the configuration management process:


